The identification features of the particular slide with little explanation is given. The points in bold are specific features for a particular system and for a particular tissue
Trachea:
Stomach fundus:
Stomach pylorus:
Duodenum:
Jejunum:
Ileum:
Large intestine:
Appendix:
Liver:
Gallbladder:
Pancreas:
Ureter:
Urinary bladder:
Pituitary gland:
 |
| TRACHEA |
Trachea:
- Mucosa- pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium surrounded by lamina propria
- Submucosa- connective tissue with seromucous tracheal glands, blood vessels, lymphatics, nerves
- Fibromusculocartilaginous layer- anteriorly C-shaped hyaline cartilage, posteriorly two ends attached by fibrous tissue and smooth muscle (trachealis)
- Hyaline cartilage- covered with perichondrium, homogeneous matrix due to same refractive index of ground substance and collagen fibers, cell nest surrounded by territorial matrix, interterritorial matrix between cell nests
- Adventitia- loose connective tissue with blood vessels, lymphatics, nerves
Lung:
- Made up of intrapulmonary bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli
- Intrapulmonary bronchi (secondary and tertiary bronchi)- pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium, surrounded by smooth muscle, islands of cartilage plates, adventitia
- Bronchioles- columnar to low cuboidal epithelium from proximal (bronchiole) to distal end (respiratory bronchiole) surrounded by thin layer of smooth muscle
- Alveoli- type I pneumocytes (simple squamous cells, for diffusion), type II pneumocytes (great alveolar cells, secrete surfactant), macrophages (phagocytosis) surrounded by connective tissue fibers with fibroblasts and capillaries
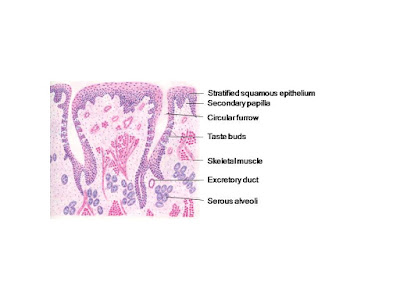
Tongue:
- Layers from superficial to deep- epithelium, lamina propria, skeletal muscle core
- Mucosa- partially keratinized stratified squamous epithelium deep to which is lamina propria
- Dorsal surface- surface projections forming papillae- filiform, fungiform and circumvallate papillae with taste buds
- Filiform papillae- present throughout the dorsal surface, conical in shape with core of lamina propria covered by stratified squamous keratinized epithelium.
- Fungiform papaillae- present mainly at the tip and sides of dorsal surface, mushroom shape with core of lamina propria covered by stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium. Taste buds are present at the surface
- Circumvallate papillae- 8-12 in number arranged anteriorly along the V-shaped sulcus, core of lamina propria surrounded by stratified squamous non keratinized epithelium, base is narrow, surface is broader. Each papilla is surrounded all over by deep furrow, side walls present taste buds extending completely through the epithelium, serous glands (von Ebner's glands) open into the base of furrow
- Taste buds- oval in shape, small opening present at the surface called taste pore, has 3 types of cells (taste or gustatory cells, supporting or sustentacular cells, basal cells)
- Core of the tongue- skeletal muscles intermingling with connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, lymphatics
Esophagus:
- 4 layers from deep (lumen) to superficial- mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, adventitia or serosa
- Mucosa- stratified squamous nonkeratinized epithelium surrounded by lamina propria and muscularis mucosa
- Submucosa- dense irregular connective tissue, mucosal (esophageal)glands , blood vessels, nerves and lymphatics
- Muscularis externa- upper 1/3rd skeletal muscle, middle 1/3rd both skeletal and smooth muscle, lower 1/3rd smooth muscle
- Adventitia- loose connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, adipose tissue
 |
| STOMACH FUNDUS |
Stomach fundus:
- 4 layers from deep (lumen) to superficial- mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa
- Mucosa- simple columnar epithelium surrounded by lamina propria (filled with long tubular gastric glands) and muscularis mucosae
- Gastric glands open into gastric pits which are short (1/4th of thickness of mucosa)
- cells in glands- mucous neck cells, chief cells, parietal cells, enteroendocrine cells
- Submucosa- dense irregular connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves and lymphatics
- Muscularis externa- inner oblique, middle circular, outer longitudinal smooth muscle
- Serosa- simple squamous mesothelium surrounding the connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, adipose tissue
 |
| STOMACH PYLORUS |
Stomach pylorus:
- 4 layers from deep (lumen) to superficial- mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa
- Mucosa- simple columnar epithelium surrounded by lamina propria (filled with coiled tubular pyloric glands) and muscularis mucosae
- Pyloric glands open into gastric pits which are long (3/4th of thickness of mucosa)
- cells in glands- mainly mucous cells, enteroendocrine cells
- Submucosa- dense irregular connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves and lymphatics
- Muscularis externa- inner oblique, middle circular, outer longitudinal smooth muscle
- Serosa- simple squamous mesothelium surrounding loose connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, adipose tissue
 |
| DUODENUM |
Duodenum:
- 4 layers from deep (lumen) to superficial- mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, adventitia or serosa
- Mucosa- simple columnar epithelium with few goblet cells surrounded by lamina propria (filled with intestinal glands/ crypts of Lieberkuhn) and muscularis mucosae
- Plicae circularis (mucosal elevations with core of submucosa) numerous,
- Villi (permanent mucosal folds with lymphatic capillary lacteal) long/tall, broad, numerous
- Submucosa- dense irregular connective tissue, duodenal glands (Brunner's glands), blood vessels, nerves and lymphatics
- Muscularis externa- inner circular, outer longitudinal smooth muscle
- Serosa- simple squamous mesothelium surrounding connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, adipose tissue
 |
| JEJUNUM |
Jejunum:
- 4 layers from deep (lumen) to superficial- mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa
- Mucosa- simple columnar epithelium with more goblet cells than duodenum surrounded by lamina propria (filled with intestinal glands/ crypts of Lieberkuhn) and muscularis mucosae
- Plicae circularis less than duodenum
- Villi shorter, narrow, and fewer than duodenal villi
- Submucosa- dense irregular connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves and lymphatics
- Muscularis externa- inner circular, outer longitudinal smooth muscle
- Serosa- simple squamous mesothelium surrounding connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, adipose tissue
Ileum:
- 4 layers from deep (lumen) to superficial- mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, adventitia or serosa
- Mucosa- simple columnar epithelium with more goblet cells surrounded by lamina propria (filled with intestinal glands/ crypts of Lieberkuhn) and muscularis mucosae
- Plicae circularis very few,
- Villi very few, shorter and narrower than duodenal and jejunal villi,
- Submucosa- dense irregular connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves and lymphatics.
- Payer's patches (Aggregations of lymphatic nodules) in lamina propria and submucosa
- Muscularis externa- inner circular, outer longitudinal smooth muscle
- Serosa- simple squamous mesothelium surrounding connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, adipose tissue
 |
| LARGE INTESTINE |
Large intestine:
- 4 layers from deep (lumen) to superficial- mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, adventitia or serosa
- Mucosa- simple columnar epithelium with numerous goblet cells surrounded by lamina propria (filled with intestinal glands/ crypts of Lieberkuhn) and muscularis mucosae
- Plicae circularis and Villi absent. Temporary folds in undistended colon
- Submucosa- dense irregular connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves and lymphatics
- Lamina propria and submucosa filled with abundant diffuse lymphatic tissue
- Muscularis externa- inner circular, outer longitudinal smooth muscle condensed into three muscular bands called taeniae coli
- Serosa- simple squamous mesothelium surrounding connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, adipose tissue
 |
| APPENDIX |
Appendix:
- 4 layers from deep (lumen) to superficial- mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, adventitia or serosa
- Mucosa- simple columnar epithelium with numerous goblet cells surrounded by lamina propria (few intestinal glands/ crypts of Lieberkuhn) and interrupted muscularis mucosae
- Submucosa- dense irregular connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves and lymphatics
- Lamina propria and submucosa filled with abundant diffuse lymphatic tissue and solitary lymphatic nodules disrupting muscularis mucosae
- Muscularis externa- inner circular, outer longitudinal smooth muscle
- Serosa- simple squamous mesothelium surrounding connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, adipose tissue
 |
| LIVER |
Liver:
- Covered by connective tissue capsule (Glisson's capsule)
- Hepatic lobule- central vein surrounded by plates of liver cells (hepatocytes) and sinusoids radiating towards periphery
- Portal triad- 3 to 6 per lobule present at periphery containing branches of hepatic artery, hepatic portal vein and bile duct
- Sinusoids lined by fenestrated endothelial cells and Kuppfer cells / liver phagocytes (detoxify blood).
- Perisinusoidal space of Disse- space between hepatocytes and sinusoids
- Hepatic cells- 6 surfaces, 4 sides related to bile canaliculi, 2 surfaces to sinusoids
- Space of Mall- space between portal canal and hepatocytes
 |
| GALLBLADDER |
Gallbladder:
- 3 layers from deep (lumen) to superficial- mucosa, muscularis, adventitia or serosa
- Mucosa- tall columnar epithelium with lamina propria. Muscularis mucosae and submucosa absent
- Temporary mucosal folds in nondistended state which may invaginate deep into lamina propria forming diverticula or crypts (Rokitansky-Aschoff sinus)
- Muscularis- randomly oriented smooth muscle fibers and interlacing elastic fibers
- Serosa covers free surface (simple squamous mesothelium surrounding connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, adipose tissue) and adventitia covers attached surface (connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, adipose tissue)
 |
| PANCREAS |
Pancreas:
- Exocrine part- closely packed serous acini with centroacinar cells which are parts of intercalated ducts
- Endocrine part- islets of Langerhans/ pancreatic islets with alpha cells, beta cells, delta cells and pancreatic polypeptide cells
- Centroacinar cells- cells of intercalated duct projecting into the serous acini
- Serous acini- small lumen with surrounding pyramidal cells having round nucleus at the lower 1/2 of the cell and protein secreting zymogenic granules at upper half
- Islets of Langerhans- thin connective tissue capsule separates the islets from exocrine part, cells arranged in cords or clumps with connective tissue fibers and capillary network. alpha cells secrete glucagon, beta cells secrete insulin
 |
| KIDNEY |
Kidney:
- It is divided into outer cortex and inner medulla
- Cortex- proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), distal convoluted tubule (DCT), renal corpuscle, medullary rays, interlobular arteries and veins
- Medullary rays- straight portions of PCT and DCT, blood vessels and collecting tubules
- Medulla (renal pyramids)- base directed towards cortex and apex (renal papilla) towards minor calyx. It has straight portions of PCT and DCT, loop of Henle
- Structural and functional unit of kidney is nephron. It has renal corpuscle (tuft of capillary plexus called glomerulus surrounded by double layer of epithelial cells called Bowman's capsule), PCT, loop of Henle (thick descending portion of PCT, thin descending and ascending segment, thick ascending portion of DCT), DCT which opens into collecting tubule.
- Lining epithelium- parietal layer of Bowman's capsule (simple squamous epithelium), visceral layer of Bowman's capsule (modified epithelial cells called podocytes), PCT (simple cuboidal cells surrounding small uneven lumen), DCT (low cuboidal cells surrounding larger lumen), loop of Henle (simple squamous cells), collecting tubule (cuboidal cells)
- Juxtaglomerular apparatus- present at vascular pole, juxtaglomerular cells (modified smooth muscle cells of afferent glomerular arteriole), macula densa (narrow numerous columnar cells in DCT), messangial cells
 |
| URETER |
Ureter:
- 3 layers from deep (lumen) to superficial- mucosa, muscularis, serosa
- Mucosa- transitional epithelium surrounded by lamina propria (fibroelastic connective tissue). Muscularis mucosae and submucosa absent
- Muscularis- inner longitudinal and outer circular smooth muscle layers. In lower 1/3rd it has one more layer outer longitudinal smooth muscle layer
- Serosa- thin connective tissue layer with mesothelium
 |
| URINARY BLADDER |
Urinary bladder:
- 3 layers from deep (lumen) to superficial- mucosa, muscularis, serosa
- Mucosa- thrown into temporary mucosal folds lined by transitional epithelium surrounded by lamina propria (fibroelastic connective tissue). Muscularis mucosae and submucosa absent
- transitional epithelium- basal layer of low columnar or cuboidal cells, intermediate layers of polyhedral cells, superficial layer of large cuboidal cells. the superficial cells are covered by plasma membrane.
- In distended state the superficial layers become flattened and the number of layers reduces to 2 or 3. The mucosal folds disappear.
- Muscularis- very thick, inner longitudinal, middle circular and outer longitudinal smooth muscle layers which cannot be distinguished.
- Serosa (thin connective tissue layer with mesothelium) covering the superior surface and adventitia (thin connective tissue layer) covering the inferior surface
 |
| PITUITARY GLAND |
Pituitary gland:
- Adenohypophysis- pars distalis, pars tuberalis, pars inermedia
- Pars distalis- Cells depending on staining
- chromophobes (50%),
- chromophils
- acidophils- somatotrophs (somatotropin), mammotrophs (prolactin)
- basophils- thyrotrophs (thyroid stimulating hormone), gonadotrophs (follicle stimulating hormone, leutinizing hormone, testosterone), corticotrophs (adrenocorticotrophic hormone)
- Pars intermedia- colloid filled vesicles surrounded by cells secreting melanocyte stimulating hormone
- Neurohypophysis- median eminence, infundibulum, pars nervosa
- Pars nervosa- unmyelinated axons arising in hypothalamus, dilated terminal end for storing hormones oxytocin and vasopressin (Herring bodies), pituicytes
 |
| THYROID GLAND |
Thyroid gland:
- Structural and functional units are thyroid folllicles lined by follicular cells and colloid in the lumen
- Follicular cells vary in shape- Hyperactive state- columnar cells, normal state- cuboidal cells, inactive state- squamous cells
- Parafollicular cells either present in between the follicles or in the follicles (between follicular cells and basement membrane)
 |
| SUPRARENAL GLAND |
Adrenal/ suprarenal gland:
- Cortex- 3 layers, zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata, zona reticularis
- zona glomerulosa- cells arranged in ovoid groups or clumps, secrete mineralocorticoids
- zona fasciculata- cells arranged vertically in columns, secrete glucocorticoids
- zona reticularis- cells arranged in network of cords or clumps, secrete sex hormone
- Medulla- cells are modified postganglionic sympathetic neurons, secrete catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine)
 |
| TESTES |
Testes:
- Numerous cross-sections of seminiferous tubules surrounded by interstitial connective tissue with fibroblast, muscle like cells, bloodvessels, nerves and lymphatics
- Seminiferous tubule- stratified germinal epithelium with spermatogenic cells and sustentacular cells (supporting/ Sertoli cells)
- Interstitial cells of Leydig present between seminiferous tubules produce testosterone
Epididymis:
- Numerous cross-sections of duct lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelium with tall columnar (principal) cells having stereocilia and basal cells
- Duct surrounded by thin smooth muscle layers and connective tissue
 |
| VAS DEFERENS |
Vas deferens/ ductus deferens:
- Mucosa- pseudostratified columnar epithelium with stereocilia surrounded by lamina propria
- Muscularis- inner longitudinal, middle circular, outer longitudinal smooth muscle layers
- Adventitia- connective tissue with numerous blood vessels, nerves and lymphatics
 |
| PROSTATE |
Prostate:
- It has glandular and fibromuscular part
- Glandular part- branched tubuloacinar glands lined by simple columnar or pseudostratified columnar epithelium. Prostatic concretions seen in acini
- Fibromuscular stroma- smooth muscle bundle and connective tissue fibers surround the glandular part
- Prostatic concretions or corpora amylacea- prostatic secretions calcified
 |
| UTERUS |
Uterus:
- 3 layers from inside out- endometrium, myometrium, perimetrium
- Endometrium-
- stratum functionalis with uterine glands and blood vessels which will be sloughed off during menstruation
- stratum basalis with remnants of uterine glands and blood vessels
- Myometrium- very thick smooth muscle layer
- Perimetrium- serosa or adventitia
 |
| UTERINE TUBE |
Uterine tube/ fallopian tube:
- 3 layers- mucosa, muscularis, serosa
- Mucosa- extensive mucosal folds, lined by simple columnar ciliated and non ciliated (peg cells) epithelium. It is surrounded by lamina propria
- Muscularis- inner circular and outer longitudinal smooth muscle layers
- Serosa- connective tissue with mesothelium
 |
| OVARY |
Ovary:
- Cortex- different stages of follicles (primordial, primary, secondary and tertiary/ mature follicles), corpus luteum, corpus albicans, attretic follicles
- Medulla- connective tissue with numerous blood vessels, nerves and lymphatics
 |
| CORNEA |
Cornea:
- Corneal epithelium- stratified squamous non keratinized epithelium
- Bowman's membrane/ anterior limiting membrane- thick homogeneous layer supports basement membrane
- Substantia propria/ corneal stroma- parallel bundles of collagen fibers and flat fibroblasts
- Descemet's membrane/ posterior limiting membrane- thick basement membrane of posterior epithelium
- Posterior epithelium/ corneal endothelium- simple squamous or low cuboidal epithelium
 |
| RETINA |
Retina:
- Pigment epithelium
- Layer of rods and cones
- outer limiting membrane- processes of Muller's cells
- Outer nuclear layer- nuclei of rods and cones
- Outer plexiform layer- synapse between axons of rods and cones, dendrites of bipolar and horizontal cells
- Inner nuclear layer- nuclei of bipolar, horizontal, amacrine and Muller's cells
- Inner plexiform layer- synapse between axons of bipolar cells, dendrites of amacrine and ganglionic cells
- Ganglionic cell layer- nuclei of ganglionic cells and neuroglia
- Nerve fiber layer- axons of ganglionic cells, inner fibers of Muller's cells
- Inner limiting membrane- termination of inner fibers of Muller's cells
Cerebrum:
- Molecular layer- neuroglial and horizontal cells of Cajal
- External granular layer- neuroglial and small pyramidal cells
- External pyramidal layer- medium sized pyramidal cells, neuroglial cells
- Internal granular layer- small granular cells, medium sized pyramidal cells, neuroglia
- Internal pyramidal layer- large sized pyramidal cells, neuroglia
- Multiform layer- fusiform cells, stellate cells, cells of Martinotti
 |
| CEREBELLUM |
Cerebellum:
- Molecular layer- stellate cells, basket cells, dendrites of Purkinje cells, axons of granule cells, basket cells
- Purkinje cell layer- single layer of Purkinje cells
- Granular layer- granule cells, Golgi type II cells, glomeruli
- Glomeruli- synapse between rosette (dilated terminal of mossy fiber), dendrite of granule cell, axon of Golgi type II cell, neuroglia
- Inner core of white matter- climbing fibers, mossy fibers, axons of Purkinje cells



Hello! I was wondering where these beautiful images come from. Are they from a histology textbook? Could you please provide me with its name? Thank you very much! --Linghua
ReplyDeleteThank you so much for the beautiful comment. These diagrams were drawn from DiFiore during my PG course for my record.
DeleteVery nice
ReplyDelete